In today’s rapidly evolving world, technology is at the forefront of transformative changes, reshaping various aspects of our lives, including the economy. One of the most profound technological advancements is artificial intelligence (AI) and its subset, generative intelligence. However, the integration of this technology into the economy is transforming it in a fast phase. Consequently, we explore how these intelligent technologies are revolutionising or changing the economy, their essential role in achieving the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), and how they align with the concept of “Thrivability.”
Source: Berkeley
What is Technology And How Is It Changing the Economy?
Technology encompasses innovations, tools, and systems that facilitate the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. The economy refers to creating and exchanging goods and services within a society. In addition to this, the relationship between technology and the economy is integral as technological advancements drive economic growth by increasing efficiency, reducing costs, and creating new industries. Moreover, technological innovation plays a crucial role in economic development by enhancing productivity, fostering innovation, and driving overall growth (Anelli et al., 2017). Furthermore, technology and the economy have a mutually beneficial relationship (Popp, 2012). Technological advancements contribute to economic development by fueling innovation and improving productivity. On the other hand, economic growth provides the necessary resources and market demand for technological innovation to thrive.

Source: ABS
Changing the Economy moving forward
As we move forward into the era of AI and generative intelligence, we find ourselves on the cusp of a profound transformation that promises to reshape the fabric of our economic landscape. These technologies represent more than just a leap forward; they herald a paradigm shift that will affect every aspect of our lives. Let’s delve deeper into the transformative power of AI and generative intelligence and their far-reaching implications (Mazilescu, 2018).
A Revolution In Work And Production:
First and foremost, AI and generative intelligence are changing the way we work and produce goods and also changing the economy as a whole. Automation, powered by AI, is already streamlining manufacturing processes, reducing labour costs, and improving efficiency. However, robots and intelligent systems work alongside human factory employees, increasing productivity and precision (Alemie, 1998). Consequently, this transformation isn’t limited to manufacturing; it extends to various sectors, including agriculture, logistics, and creative industries. The nature of work is evolving, with humans collaborating with machines in novel ways.
The Changing Economy: New Age Communication
Secondly, communication is integral to our daily lives, and AI is revolutionising this sphere. Chatbots, virtual assistants, and language translation AI have made communication easier across linguistic and geographic barriers. In addition to that, social media platforms and online content are increasingly curated and personalised using AI algorithms, enhancing user experiences (Labazanova et al, 2023). Additionally, generative intelligence is being applied to create new modes of communication, from AI-generated content to deepfake technology, offering exciting opportunities and ethical challenges, ultimately changing the economy.

Source: Brookings
Reimagining Education And Lifelong Learning:
Third, the education sector is experiencing a significant shift thanks to AI. Moreover, personalised learning platforms powered by AI adapt to individual student needs, providing a tailored educational experience. However, lifelong learning is becoming more accessible, with online courses and media that use AI to offer continuous education and upskilling opportunities. AI expands access to education and transforms how we learn and acquire new skills (Tiwari et al, 2022).
The Role Of AI And Generative Intelligence In Innovation:
Innovation is at the heart of progress, and AI and generative intelligence are pivotal in driving creativity and invention. These technologies offer new creative avenues, from AI-generated art and music to innovative product design. In other words, AI’s predictive capabilities help researchers and inventors identify trends and potential solutions, accelerating innovation. (Alemie, 1998).
Ethical Considerations And Societal Implications:
As we navigate this transformative era, we must also grapple with the ethical considerations and societal implications of AI and generative intelligence. Questions about data privacy, bias in AI algorithms, and the impact of automation on employment need to be addressed. Moreover, the potential for misuse, such as deepfake technology, requires careful regulation and oversight (Tiwari, 2022).

Technology’s Economic Impact Matters
Understanding the impact of AI and generative intelligence on the economy is not merely an intellectual exercise; it’s a necessity for several profound reasons. The following points elaborate on the significance of this focus:
Economic Transformation and Growth:
Adopting AI and generative intelligence represents a fundamental shift in businesses and industries’ operations. In addition to that, these technologies optimise production processes, increase efficiency, and reduce operational costs. As a result, they have the potential to revolutionise existing industries while creating entirely new economic opportunities. This transformation drives economic growth, generates jobs in emerging fields, and enhances prosperity (Mazilescu, 2018).
Addressing Global Challenges In The Changing Economy:
AI and generative intelligence are pivotal in addressing the most pressing global challenges, including sustainability, healthcare, and education. Consequently, embracing these technologies is essential for achieving the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Here’s how:
- Sustainability: Firstly, AI aids in optimising resource management, increasing energy efficiency, and supporting sustainable practices in industries. By reducing waste and environmental impact, AI contributes to SDGs such as Affordable and Clean Energy (Goal 7) and Responsible Consumption and Production (Goal 12).
- Healthcare: Secondly, AI-powered solutions improve diagnostics, drug discovery, and patient care. This directly impacts Good Health and Well-being (Goal 3) and contributes to universal healthcare access (Tiwari, 2022).
- Education: Thirdly, AI’s personalised learning platforms enhance access to quality education and promote lifelong learning, aligning with Quality Education (Goal 4) (Tiwari, 2022).
Ensuring Inclusivity:
As the world evolves in the digital age, there is a growing concern about the digital divide. Ensuring that AI and generative intelligence benefit all segments of society is crucial. By focusing on how these technologies change the economy, we can strive for policies and strategies that promote inclusivity, making the benefits accessible to all, regardless of background or location (Saida Labazanova et al, 2023).
Policy Development:
Moreover, understanding how AI and generative intelligence affect the economy is fundamental for policy development. Policymakers must create a regulatory framework that encourages innovation while protecting against potential misuse. However, informed decision-making can lead to a balance that supports economic growth and societal well-being (Tiwari, 2022).
Preparing The Workforce:
Furthermore, AI and generative intelligence reshape industries, and there is a growing need to prepare the workforce for these changes. This includes reskilling and upskilling programs, fostering digital literacy, and adapting education systems to the evolving demands of the job market (Saida Labazanova et al, 2023).
Ensuring Economic Resilience In the Changing Economy:
By focusing on how these technologies change the economy, we can work towards building economic resilience. Moreover, AI and generative intelligence can enhance predictive capabilities, helping industries prepare for economic disruptions and unforeseen challenges. This resilience is crucial for the stability of both local and global economies (Saida Labazanova et al, 2023).
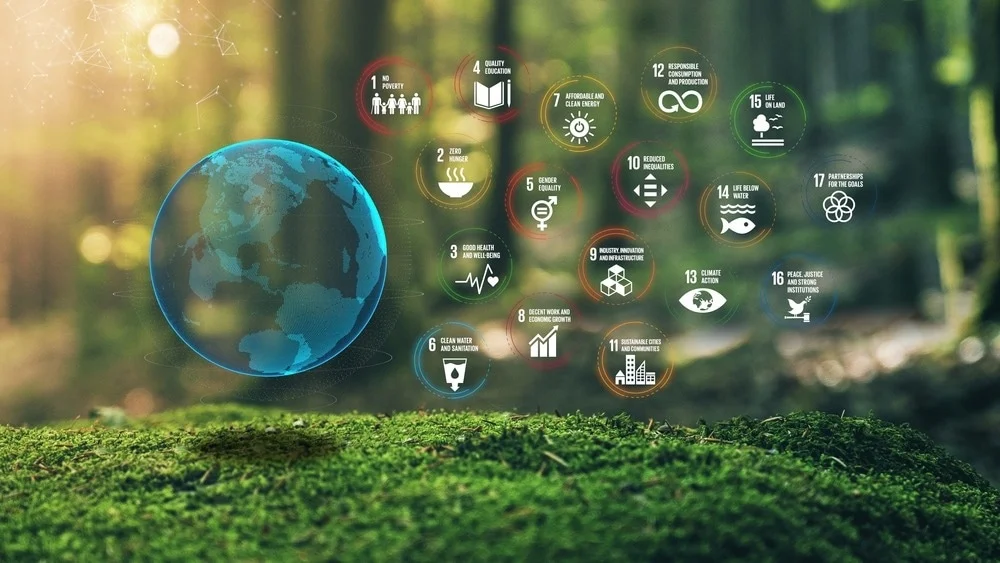

achieving the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and how they link to How Technology Is Changing The Economy
AI and generative intelligence are powerful tools for advancing the SDGs. (Popp, 2012). For instance:
Sustainability: Firstly, AI can optimise energy consumption, manage resources more efficiently, and support sustainable agriculture, contributing to several SDGs, including (Goal 7) (Affordable and Clean Energy) and (Goal 12) (Responsible Consumption and Production).
Education: Secondly, AI-powered personalised learning platforms can improve access to quality education (Goal 4) and promote lifelong learning.
Healthcare: Thirdly, AI-driven healthcare solutions can enhance accessibility and quality, aligning with Goal 3 (Good Health and Well-being) (Popp, 2012).
Generative Intelligence and Creativity: Finally, Generative intelligence can foster creativity and innovation, which is essential for addressing various SDGs, including Goal 9 (Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure) and (Goal 11) (Sustainable Cities and Communities).
A Thrivable Framework
The concept of “thrivability” aligns seamlessly with the potential of AI and generative intelligence in the economy:
Thrivability and Economic Prosperity: Firstly, Thrive recognises that AI and generative intelligence can drive economic prosperity by enhancing productivity, innovation, and access to economic opportunities. THRIVE-Platform
Sustainable Solutions: Thirdly, Thrive promotes the idea that AI and generative intelligence can lead to sustainable solutions that prevent disasters and offer the potential for flourishing societies. youtube
Predictive Analyses: Furthermore, The Thrive Framework evaluates potential solutions through predictive analyses, utilising AI’s capabilities to support environmental and social sustainability transformations blog
The Thrivable Zone: In addition to that, AI and generative intelligence can help find innovative solutions within the “thrivable zone,” balancing economic growth with environmental well-being.
The THRIVE Project: Finally, Thrive actively researches, educates, and advocates for the responsible use of AI and generative intelligence to achieve economic and environmental sustainability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, AI and generative intelligence drive transformative changes in the economy, offering unprecedented opportunities for growth and sustainability. Moreover, embracing these technologies is essential for achieving a thriving and equitable future. However, we can address global challenges, enhance economic well-being, and work towards a more prosperous and sustainable world by harnessing AI and generative intelligence.

















