Within the finance sector, sustainable infrastructure has never been the main focus for financial institutions. The focus is on traditional infrastructure that yields economic or financial gains for many institutions such as banks and investment companies. However, over time the investment and financing in traditional infrastructure has given rise to negative social and environmental impacts. By altering natural water flows in rivers, dams, and wetlands, traditional infrastructure causes rising global temperatures, biodiversity loss, and droughts. Moreover, droughts as a result of climate change have caused the drying and dying of coastal dunes.

Technological advances and infrastructure development, to meet population growth demands, have raised global concerns about climate change today. As a result, businesses across sectors, including finance, seek ways to incorporate environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors into their offers. However, the finance sector is the last to respond to climate change in comparison to other sectors.
The finance sector has no choice but to respond to climate change. The current infrastructure financing model does little to benefit the world, more companies are shifting towards sustainable infrastructure. As a result, the financial sector sees the need to finance sustainable infrastructure. Otherwise, financial institutions will lose out as companies seek funding elsewhere, supporting their sustainability efforts. The finance sector is compelled to reconsider and revise the current regulations on financial products and investment strategies, supporting companies to transition, while at the same time maintaining profits, and reaching sustainability goals and the Paris Agreement target plans of net zero carbon by 2050.
What is Meant By infrastructure in the finance sector?
To define sustainable infrastructure in the finance sector, we must first explain the meaning of infrastructure. Infrastructure refers to the physical facilities required to ensure the proper functioning of a business, a community, or society in an economy.
The Definition Of Sustainable
Based on THRIVE Project definitions, sustainable means… “using current resources to meet needs of the current population without compromising resources for needs of the future generations“.
What is Sustainable Infrastructure?
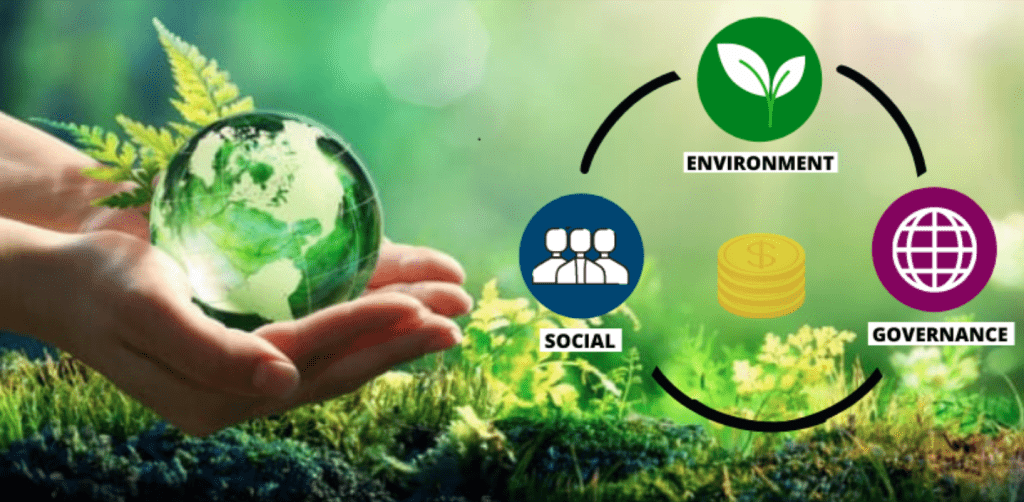

Sustainable infrastructure involves developing infrastructure to be sustainable by integrating environmental, social, and economic factors. When financial institutions integrate ESG factors into their products and services, they form a concept known as Sustainable Finance. As a result, sustainable infrastructure in the finance sector relates to financing and investment of sustainable infrastructure with ESG factors. Here is a table that shows the dissimilarities between sustainable and traditional infrastructures.
| Sector | Traditional Infrastructure | Sustainable Infrastructure |
| Energy | Nuclear power, fossil fuel (coal, gas, oil) | Solar, wind, water, & tidal |
| Transportation | Aeroplanes, trucks, cars | Electric vehicles, bicycles, carpooling |
| Real Estate | Energy consuming homes | Smart buildings |
| Waste | Landfills, incinerators | Re-use, smart waste systems, recycling |
| Mining | Underground mining | In situ mining |
Sustainable Practices In The Finance Sector
In the sustainable finance sector, financial institutions focus on financing and investing in sustainable infrastructure that supports climate change goals. Various sustainable finance products or services fund sustainable infrastructure initiatives. These sustainable solutions include:
Green & Social Bonds
Green bonds. also known as climate bonds, involve government entities, financial institutions, or corporations issuing green bonds, as debt capital. The issuance finances, or funds, sustainability-focused initiatives with positive environmental benefits. On the other hand, social bonds involve issuers issuing social bonds to finance socially impactful initiatives. For instance, these initiatives usually aim to eliminate poverty, create employment, and provide marginalised communities access to quality education.

Green Loans
Green loans involve lenders granting loans to borrowers to perform environmentally friendly activities. Although similar to green bonds, green loans typically involve smaller capital amounts with binding terms.
Green Venture Capital
Green venture capital is a green investment fund that supports mainly sustainable environmental and socially responsible businesses. The funding is to aid in the development of clean infrastructure and the removal of toxins from the earth.
Green Credit
Green credit is a sustainable finance solution to finance companies that reduce emissions and are low consumers of fossil fuel-related energy.
Impact or Responsible Investing
This is a type of investment made to promote sustainability and to gain social, financial, and environmental benefits. Additionally, impact investing provides value-based and value-driven investments. Because investors contribute to the development of a zero-carbon economy, valuable ESG data is to be considered in the investment. Conventional investing usually does not consider ESG information in the current investment strategies.
Green Insurance Products
Green insurance provides cover on flood–proofed houses, pay-as-you-drive (PAYD), and businesses to mitigate hazardous weather conditions such as droughts. Consequently, the cover helps fight climate change and promotes behavioural change in consumers in real estate, agriculture, and transport industries.
Sustainable finance aims to fund businesses reducing automobile emissions, using sustainable energy, and creating green buildings. All these contribute to positive environmental impacts while at the same time promoting social inclusivity and economic growth. In conclusion, sustainable infrastructure in the finance sector focuses on sustainable infrastructure, finance, and investments.
the benefits of sustainable infrastructure And The Finance Sector
Financing and investment in sustainable infrastructure projects can bring substantial benefits to financial institutions, producers, and consumers of sustainable products. Companies that develop or move to sustainable infrastructure ensure that businesses can commit to achieving long-term sustainability. Here are the benefits of sustainable infrastructure finance and investment:
- Reduce emissions
- Preserve natural resources
- Lower fuel costs
- Promote economic growth and green jobs
moving forward
Achieving a clean sustainable environment with a toxins-free world is the responsibility of every person, community, and institution. This includes financial institutions such as banks, development banks, and green venture capitalists. Investing in or financing sustainable infrastructure can reduce the global carbon footprint, combat climate change, and secure a sustainable, and thrivable future, for generations to come.
There are various ways companies can build sustainable infrastructures and use banks to facilitate the investment of such infrastructure, by directing finances to projects that build resilient socially inclusive infrastructure. An example of this is energy-efficient power stations, transport, and water systems, to minimise negative environmental impacts, and maintain profitable organisations. This improves communities and promotes maximum sustainable and globally conscious economic development and growth.
The inclusion of sustainable practices into investment strategies, combined with technology, aids both financial firms and companies. First, financial institutions determine profitable sustainable projects to fund. Second, they help companies seeking finance access to sustainable infrastructure investment capital. OpenInvest is a technology-using platform for responsible investment. Another company is Orbital Insight, a US-based company using geospatial data analysis technology to assist investment institutions in ensuring they invest in profitable sustainable projects. Both companies show the use of technology to promote sustainable infrastructure investments in the finance sector.
Why is it essential that we focus on sustainable infrastructure in the finance sector?
It has become an increasing necessity for financial institutions to focus on sustainable infrastructure financing as the climate crisis worsens. As financial institutions emphasise sustainable infrastructure investment, they are actively helping mitigate ESG risks that come with climate change. In the future, we need to channel more financial resources toward green initiatives with ethical sustainable practices. Investing in sustainable infrastructure ensures that resources are safe for future generations, beyond just protecting the environment.
achieving the United Nations Sustainability Development Goals (SDGs) and how they link to the finance sector
In finance, sustainable infrastructure investments play an essential role in fast-tracking the accomplishment of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). As financial institutions invest capital in smart real estate, green urban planning, and sustainable corporate or industrial building, the investments contribute to achieving SDG9 (Resilient Infrastructure for Sustainable Innovative Industries) and SDG11 (Sustainable Cities). Also, the use of sustainable materials for infrastructure development indirectly contributes to SDG12 (Sustainable Responsible Consumption).

Using sustainable materials and financing energy-efficient renewable energy reduces pollution from the environment by removing toxins in the atmosphere. As a result, people using sustainable infrastructure gain access to SDG7 (Clean, Affordable Energy). In turn, improving SDG3 (Human Health and Well-being) in the process. Moreover, funding sustainable water use resources and systems enhances SDG6 (Sanitation with Access to Clean Water for all).
As all SDGs intertwine, collaborative partnerships between financial institutions, governments, and private sectors are necessary, to advance SDG13 (Climate Action) and foster SDG8 (Decent Green Jobs for Economic Growth). Both these goals simultaneously address the global challenges of SDG1 and SDG2 (Zero Poverty & Hunger).
A Thrivable Framework
The THRIVE Framework is a holistic regenerative approach seeking to transform the sustainable efforts of organisations across the planet.
It is the mandate of THRIVE project to assist all businesses to adopt thrivable and sustainable practices. THRIVE Project aims to determine entity models and strategies linked to the well-being of organisations globally, by offering a platform where companies can measure their sustainability performance. Therefore, sustainable infrastructure in the finance sector forms a crucial link to The Thrive Framework.
The sustainable infrastructure investment impacts several dimensions of the 12 Foundational Focus Factors. One of them is integral thinking, integral thinking allows companies to prosper by including ESG factors. For instance, financial institutions direct capital to non-finite sustainable resources. Also, context-based metrics and entity models. The two factors identify what an entity does and measure the sustainability of its activities. This is useful for banks to determine if the activities are bankable (fundable) or not.
Furthermore, sustainable finance in the finance sector also ensures that value-based innovation is achieved, especially for responsible investing projects. Such investment is undertaken to place value on human health, to improve gender inequality, and fair labour laws for example. Bringing value helps to solve complex wicked problems, such as climate change and pollution caused by the financing of traditional infrastructure. Lastly, companies investing in sustainable infrastructure use the three core principles of a regenerative economy.
If you would like to learn more about Thrivability, register for our webinar events to discuss all things sustainability with experts in the field. You can sign up for our free newsletter, follow our podcast series, and informative monthly blog posts. Further educational videos can be found on our YouTube Channel.























