The rise of the BRICS group comprised of Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa has significantly developed. This growth and recent engagements with other nations changed the global economic landscape, with a combined population of over 3 billion people. As a large share of the world’s GDP, these nations have seen remarkable economic growth over the past few decades. The emergence of BRICS has challenged the dominance of traditional economic powers. It also sparked discussions on the potential implications for the global economy. THRIVE explores the key factors contributing to the rise of BRICS in the present decade, and the potential benefits and challenges of a BRICS currency if introduced. What are the implications for the changing landscape of the global economy? How does this affect Global economic growth?
What is the BRICS group?
BRICS is a group of five major emerging economies: Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa. They’re joined together to enhance their growth and collective voice in international forums and promote economic growth and development. They hold annual summits to discuss and coordinate various issues, including financial policies, trade, investment, and geopolitical matters. Despite their diverse range of economies, political systems, and cultures, the BRICS countries collectively represent a substantial portion of the world’s population and GDP.

Source: Library of Congress
BRICS Currency, Trade and Global economic growth
The establishment of a BRICS currency presents both opportunities and challenges. Reducing dependency on the US dollar and Western financial systems means that BRICS can promote economic cooperation among its member nations. They could enhance intra-BRICS trade and mitigate exchange-rate risks in bilateral trade. That could enhance their growth and global economic growth.
Recent developments like Russia and India exploring settling bilateral trade in their currencies show progress. Additionally, the interest shown by Gulf countries, like Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates, in diversifying their foreign exchange reserves away from the US dollar. This could further pave the way for a BRICS currency and lead to global economic power dynamics shifts. The monetary sovereignty that the US does have can’t be achieved by BRICS shortly.
Benefits and Challenges of a BRICS Currency
The idea of a common BRICS currency has been discussed for years, and its realisation could have significant benefits. A BRICS currency could lead to greater financial autonomy for the bloc. Which will foster economic cooperation and bolster economic ties among member countries. However, challenges related to divergent economic policies, historical rivalries, and the need for a unified monetary policy. These factors must be addressed to realise the full potential of a BRICS currency. Moreover, concerns over China’s economic policies and trade practices could affect the group’s credibility. To become a global economic powerhouse, BRICS nations must address these internal differences, promote global economic growth, and enhance cooperation.
Major Barriers to Global Economic Growth
China-Centric Dominance
The Chinese economy’s preeminence and pivotal role in trade dynamics overshadow the BRICS alliance, essentially rendering it more of a partnership centred around China rather than an equitable consortium of equal participants.
Absence of Shared Economic Interests
The BRICS nations need more cohesive economic interests. Their mutual trade stands at less than $320 billion annually, on a downward trend, in stark contrast to their work with the US and EU, which is 6.5 times higher. Furthermore, China’s global trade surpasses the combined result of all BRICS countries by 12.5. Notably, China’s trade with South Korea alone approaches that between the BRICS members. This could notably affect global economic growth and individual growth as well.
Homogeneity in Key Aspects
With significant commonalities, notably excluding Russia, the member nations hold substantial foreign reserves, ranging from 15% to 35% of their GDPs, while maintaining low external debt, varying from 15% to 37% of GDP. Additionally, most nations, save for Russia, are deeply entrenched in consumer goods production aligned with Western markets.
Intra-BRICS Competition
A noteworthy facet is the competition among BRICS nations in third-party markets. This rivalry is evident across various sectors: ranging from clothing (China, India, Brazil) to their influence on the African continent (China, South Africa, India), and even encompassing international aviation and military equipment markets (China, Russia, Brazil). This mutual competition often precludes substantial cross-country scientific collaboration due to the ease of replicating and adapting technologies.
Cultural and Prioritisation Disparities
BRICS members grapple with marked diversity in terms of cultures, phases of global economic growth and development, ideological orientations, and interpretations of poverty. This diversity has impeded the formation of shared priorities necessary for the fruitful exchange of experiences and productive cooperation.
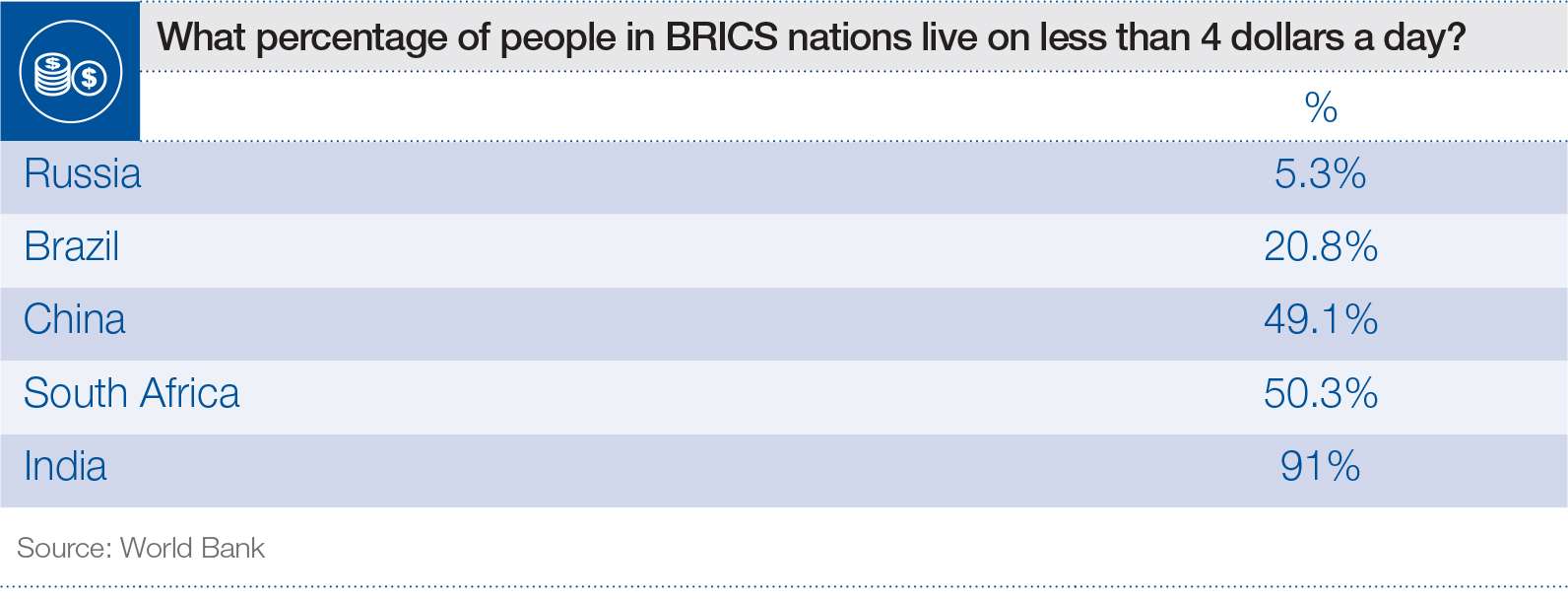
Source: World Economic Forum
Building Robust BRICS Financial Infrastructure for global economic growth
A robust financial infrastructure must be established. This is to support the successful implementation of a BRICS currency. This includes forming a BRICS Central Bank. This would formulate a unified monetary policy and coordinate interest and exchange rates among member nations. Creating a BRICS Reserve Fund can also help mitigate financial crises and provide liquidity assistance during economic downturns. Strengthening regional financial institutions is needed, such as the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) and the New Development Bank (NDB). These can further enhance economic integration and support infrastructure, development and investment within the bloc.
Fostering Economic Cooperation and Addressing Disparities
Enhancing intra-BRICS trade is essential to harness the full potential of a common currency. Lowering trade barriers, harmonising regulations, and promoting business in sectors of mutual interest can foster economic cooperation. This could enhance and bolster the economic ties among member countries. Joint infrastructure projects, technology transfers, and knowledge sharing can support sustainable development and economic growth across the BRICS bloc, addressing economic disparities and promoting inclusive prosperity. Moreover, the growing influence of the BRICS group has attracted applications for membership from other countries, leading to a more diversified and inclusive economic cooperation platform.
Navigating Geopolitical Considerations for global economic growth
While forming a BRICS currency can promote economic autonomy, geopolitical considerations must be navigated carefully. Engaging with existing international financial institutions, such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank, can provide BRICS countries with a platform to influence global economic policies and advocate for their interests. Addressing political differences through peaceful dispute-resolution mechanisms and fostering dialogue among member countries can help manage geopolitical tensions and ensure the bloc’s cohesion.
BRICS Plus
In June 2022, during the BRICS Leaders Meeting, Chinese President Xi Jinping said that adding more countries to the BRICS group is essential. Argentina and Iran officially asked to join during the meeting. Many things push for this expansion, like Western countries putting sanctions on Russia and China, more trading and investing between BRICS countries, and other nations wanting to join. Adding new countries is a big deal because it helps BRICS become more critical worldwide, have more resources, more significant markets, and more influence in world events.
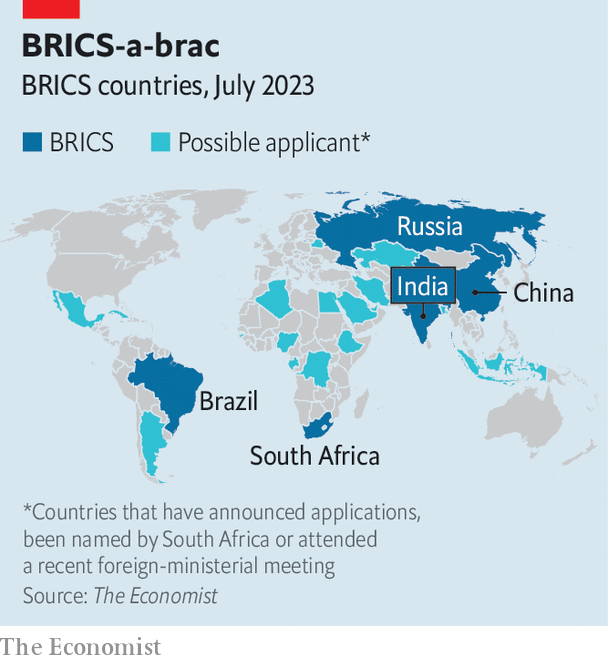
Source: The Economist
Sanctions avoidance
Western countries are putting pressure on Russia and China’s economies. So, BRICS countries are trying to strengthen their friendships and increase their power and influence worldwide. When BRICS expands, they’ll trade more, share security plans, exchange cultures, and sell weapons and software to new members. Countries like Saudi Arabia, Nigeria, Egypt, Argentina, and Indonesia want to join BRICS because they think Western countries are losing power, and see opportunities for growth and resources.
If all the countries that want to join BRICS do, the group will have almost half of the world’s population control a lot of the world’s gas, and have an economy almost twice as big as the EU’s and more significant than the US. BRICS is looking at ways to work better together, like sharing technology, giving each other better trading deals, and making rules and standards.
Middle East
BRICS countries are getting closer to Saudi Arabia, and Saudi Arabia is becoming better friends with China and Russia. This is a significant shift in the world’s economy and politics. Saudi Arabia relies less on the US and buys more weapons from China. This could cause problems between Saudi Arabia and the US. The US has been criticising Saudi Arabia, weakening their friendship. Saudi Arabia is thinking about how they should be friends with the US.
Emphasising Sustainability and Inclusivity
A BRICS currency can also catalyse promoting sustainability and inclusivity. The bloc can lead the way in environmental protection and sustainable investment by encouraging green finance and sustainable development. Moreover, advocating for the interests of developing countries in international forums and engaging with the global south can empower developing economies and create a more balanced and inclusive global economic order.
BRICS nations are major contributors to global emissions. They face emissions in three scopes: Scope 1 (direct), Scope 2 (indirect energy-related), and Scope 3 (other indirect). These impact local industries, supply chains, investment, and international ties. BRICS’ efforts to address emissions can reshape economies, trade, and diplomacy. Their significance means choices influence the global economic direction and the climate change fight. (Baloch & Ulucack, 2023).
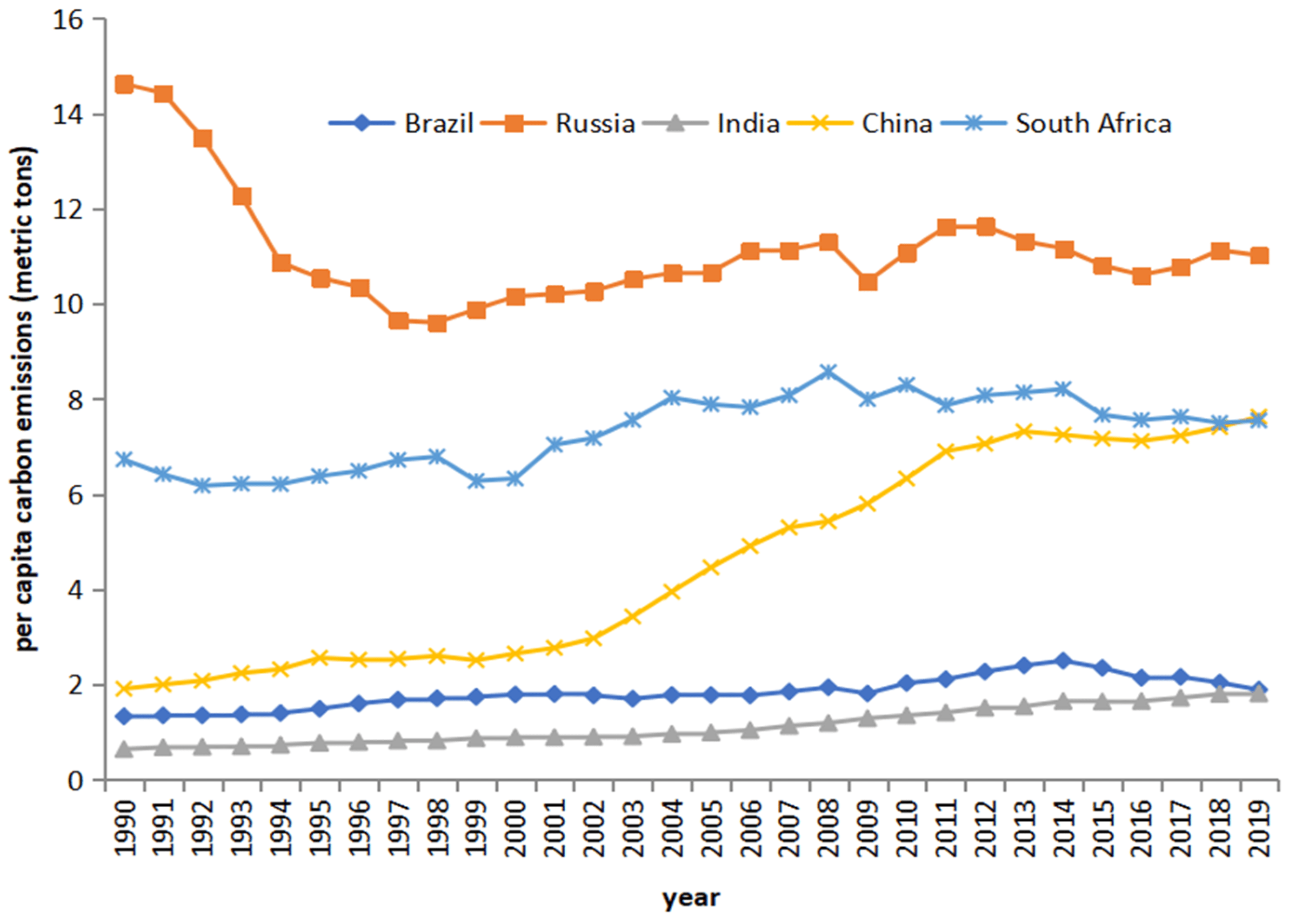
Source: MDPI
Moving Forward
The emergence of BRICS and the potential establishment of a BRICS currency represent pivotal moments in the global economic landscape. While the benefits of reduced dependency on the US dollar and enhanced economic cooperation are promising, challenges related to divergent economic policies and geopolitical tensions must be overcome. Establishing a robust financial infrastructure, fostering economic cooperation, addressing disparities, navigating geopolitical considerations, and promoting sustainability and inclusivity are crucial steps toward successfully implementing a BRICS currency. As the world witnesses the evolution of the international monetary order, the BRICS group can significantly reshape the global economic landscape and contribute to a more balanced and prosperous global economy.
In 2023, the world’s economy is changing a lot. The economy is slowing down, so new partnerships and arrangements are forming. Russia and China got sanctions from Western countries, making the global economy split more. This starts a new kind of globalisation, where Western and BRIC countries compete to be the strongest. The times of BRIC’s countries working closely with Western countries are over. Lula becoming Brazil’s leader will make Brazil move away from Western countries, especially the U.S.
China and the U.S. not getting along well makes China want to add more countries to BRICS. NATO growth in Asia tells China that it needs to create stronger ties with other Asian countries in BRICS and make its global supply chain network better. In June 2022, the meeting was about making BRICS and Western countries work together better, but now Russia and China are facing sanctions from Western countries. BRICS growth will change global trade a lot and will affect how supply chains work in the future.
why Is it essential that we focus on BRICS as a Driver of Global Economic Growth?
The BRICS nations have the potential to impact the global economy significantly. With their diverse range of industries, resources, and markets, they can collaborate to create a more balanced and diversified global economy, reducing dependence on a few economic powerhouses. The BRICS countries can foster more efficient and sustainable economic growth by opening up new trade and investment opportunities and investing in research and innovation. This will benefit the member countries and their international partners, creating a ripple effect of financial stability and growth. Addressing infrastructure needs and promoting sustainable development practices can further strengthen the economic ties among the BRICS countries. This can lead to more effective use of resources, reducing waste and promoting sustainable practices that benefit the environment.
Moreover, by working together, the BRICS countries can better influence international institutions and policies to represent the interests of emerging economies’ interests. This can lead to a more balanced global economic order where all nations’ voices are heard and considered. Strengthening economic ties among BRICS countries can contribute to geopolitical stability, creating a more peaceful global environment. The collaboration and cooperation among these nations can set an example for the rest of the world, encouraging other countries to work together towards global prosperity and peace.
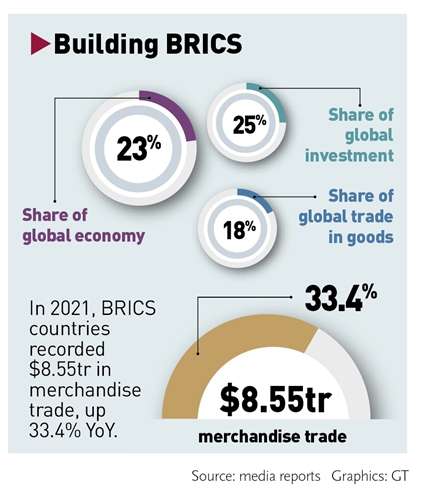
Source: Global Times
achieving the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): how they link to BRICS and global economic growth
The BRICS nations have a vital role in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) set by the United Nations. These goals cover various issues, ranging from poverty and hunger to climate change and gender equality. With their economic might and resources, the BRICS countries can bring about significant change in alignment with these objectives. By investing in sustainable agriculture, healthcare systems, clean energy, and infrastructure, they can address crucial issues like poverty, hunger, and gender disparities (Ofori & Appiah-Opoku, 2023) Moreover, their commitment to reducing inequalities, promoting innovation, and encouraging responsible consumption can aid global efforts to realise the SDGs. The BRICS nations can enhance their impact and forge partnerships to advance these common goals by collaborating closely and sharing expertise. Ultimately, this will pave the way for a more inclusive, sustainable, and prosperous world by 2030.
The BRICS countries have made significant economic growth, healthcare, and technology progress over the years. However, despite these strides, they still face significant challenges in addressing poverty, hunger, climate change, and gender equality. These issues are due to economic disparities, conflicting priorities, and the need for comprehensive policy frameworks. Collaboration and knowledge-sharing are essential to tackle these issues, but geopolitical tensions and competing priorities could hinder effective partnerships. Therefore, these countries must work together to find common ground and implement effective policies that will help them overcome these challenges.
A Thrivable Framework
As BRICS nations collaborate to establish a common currency and enhance economic cooperation, they have the potential to drive economic growth and contribute to their populations’ well-being and prosperity. Aligned with the vision, THRIVE Framework emphasises sustainability, inclusivity, and innovation. By incorporating principles from the THRIVE Framework into their initiatives, the BRICS countries can ensure that their economic growth is equitable, environmentally responsible, and socially inclusive.
As these nations navigate challenges such as geopolitical considerations and internal disparities, the THRIVE Framework provides a guiding pathway towards achieving a balanced and prosperous global economy that benefits all members of society. This alignment between the BRICS’ aspirations and the principles of thrivability highlights the potential for transformative change worldwide, ultimately shaping a more sustainable and thrivable future.























