The phrase “Death and Taxes” suggests that taxes are both inevitable and unwelcome. However, taxes serve a vital function in society. In fact, it is through taxation that we are able to make the world a better place for everyone. To explain this, let’s start at the basics.
The term tax refers to the amount of money which an individual must pay to the government. Taxation has a long history, with origins stretching back to ancient Greek and Roman civilisations. However, taxes played a minor role in these societies. But then, as complex systems started developing, human requirements increased. This meant that taxes started to become a key factor in determining the economy of a country.
Types of taxation
There are two classes of tax; which are direct taxes and indirect taxes.
- Direct taxes – Tax paid directly to the government that imposes it. Some common examples of this are income tax, property tax or taxes on assets.
- Indirect tax – Tax imposed on a manufacturer or a supplier, who then passes on the tax to the consumer. Examples include Value Added Tax (VAT) or an excise tax on alcohol and cigarettes. There are also pollution taxes, such as a carbon tax.
Why do we pay taxes?
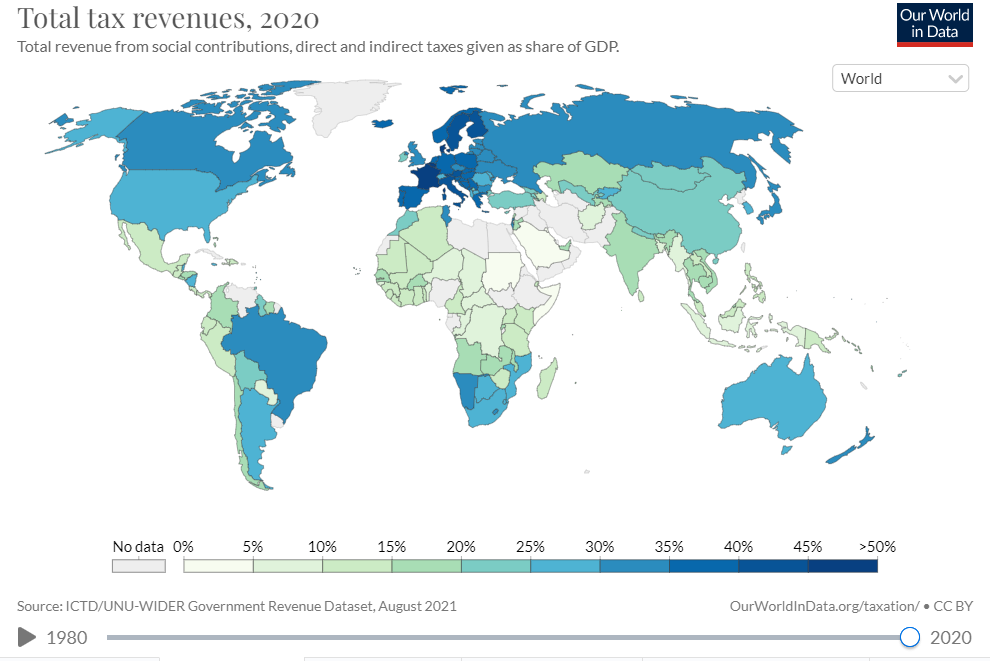
Governments require funds to provide the community services such as education, health, defence, and infrastructure. They collect the money through taxes, which is also referred to as revenue. Governments use taxes to fund research, environmental protection, pensions, and unemployment benefits. Furthermore, taxes contribute to the gross domestic product (GDP) of a country.
Income tax is one of the main sources of a government’s revenue. The term refers to payments which a government imposes on an individual or business. The amount taxed is based on income generated by the individual or business. This tax funds education, health, security and provides infrastructure facilities. For this reason, most countries have an income tax system.
Tax Compliance
To practice tax compliance is to act in accordance with tax laws and regulations. This often means paying accurately, and on time. It is thus important for any individual or business to plan their tax payments. Some things tax plans consider include:
- The size and timing of purchases
- Expense planning
- Deduction and credit opportunities

Planning the tax payments will provide short- and long-term benefits such as…
- Retirement planning for individuals, thus maximising savings and economic stability
- Saving time and reducing errors, ultimately decreasing overall tax liability
There are online tools from government tax departments, banks and tax consultants to calculate taxes. These include the International Tax calculator from Thomson Reuters, the Australian Taxation office (ATO), Suncorp (Australia) and H&R BLOCK.
Tax evasion
Tax evasion or tax fraud is an illegal activity where one deliberately avoids paying a true tax liability. As such, people who commit this crime are subjected to criminal charge. Accordingly, they could face substantial penalties. Examples of ways people evade tax include:
- Failing to reveal income accurately
- Underreporting income
- Deliberately underpaying taxes
- Increasing the expenses and deductions
- Hiding money
Fairness of taxes imposed, tax knowledge and moral obligation are some factors that influence taxpayers to engage in tax evasion.
Finally, government tax office can apply penalties, if one fails to meet a tax obligation. Such penalty rates can differ according to the country. Overall, tax evasion reduces the tax revenue to governments. This can consequently weaken the economy and destabilise the financial systems.
Tax evasion vs tax avoidance
Unlike tax evasion, tax avoidance differs in that it is compliant with the law. Instead of unlawful behaviours, it involves legitimately minimising taxes. This can occur through taking tax credits (such as paid family leave to employees) or setting up tax deferral plans. Claiming allowed tax deductions is a common tactic in tax avoidance.
Examples of this process include:
- Home office expenses
- Vehicle and travel expenses
- Gifts and donations
- Investment income
The biggest issue with tax avoidance is tax havens. These are places where wealthy people keep money in offshore accounts. Tax havens have cost governments $200 billion a year in lost global tax revenue. About 40% of multinational profits are shifted to tax havens. Most of these major tax havens are located in British Virgin Islands, as well as the Bermuda and Cayman islands. Tax havens with private wealth are mostly located in Switzerland, USA and Cayman Islands.

The Panama papers and Luxembourg leaks revealed who uses these tax havens. This then led the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) to launch two projects to counter these. These projects are Common Reporting Standard (CRS) and Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS) project. CRS aims to help authorities track offshore holdings of their taxpayers. Likewise, BEPS works to improve the transparency of multinational corporations. In essence, it wants to realign taxation with economic substance.
Socioeconomic impacts of tax avoidance
Clearly, taxation is a powerful tool that can help governments achieve SDGs. However, tax evasions and avoidance are hidden causes of inequality and poverty. Thus, governments need to maintain strict tax regulation policies. We require those policies to promote investments, job opportunities and economic growth. Taxation is essential to mobilise domestic resources and strengthen the country’s infrastructure.
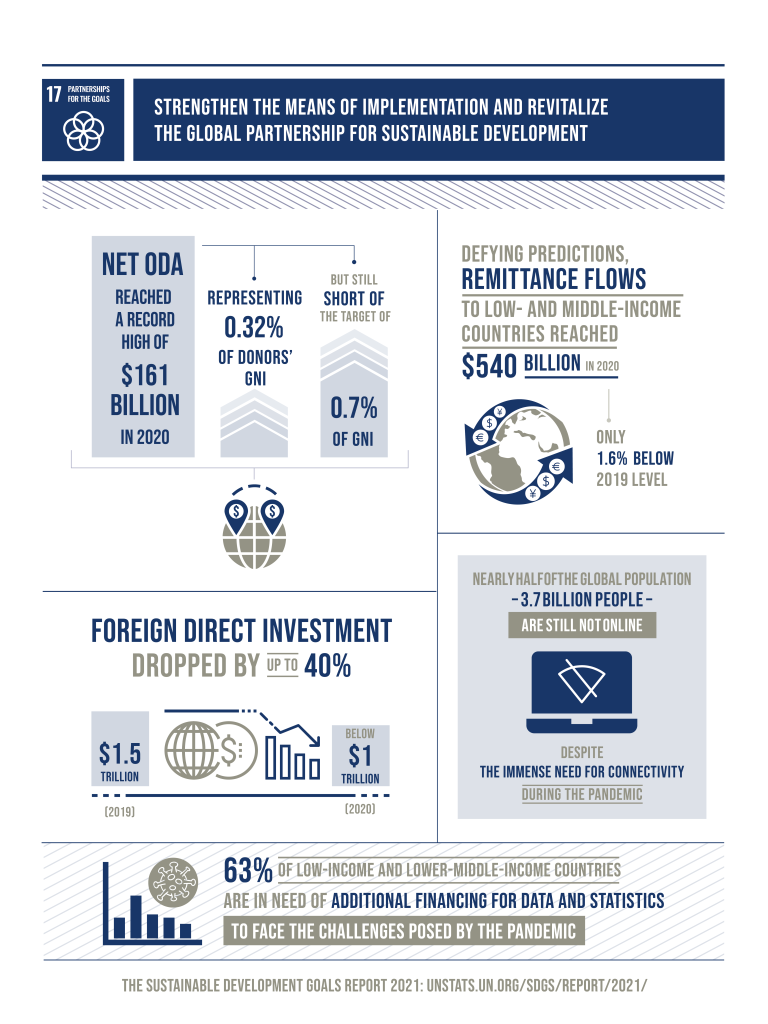
In 2020, remittance flows to low and middle income families reached $540 billion. Foreign direct investment dropped by 40% in the same year. To achieve the SDG 17 goal of global partnerships, we must provide international support to developing countries. To do so, we need to improve domestic capacity for tax and other revenue collection.
Taxes play an important role in the sustainable development of any country. Therefore, having proper tax systems and policies is essential to avoid any tax fraud. For more information on other similar issues that exist on our planet, visit our THRIVE blog. Here we share more information on the problems our world faces and offer solutions.




















